

Patients with cerebellar damage suffer from balance disorders, and they often develop stereotyped postural strategies to compensate for this problem (e.g., a wide-based stance).Ĭoordination of voluntary movements. Through its input from vestibular receptors and proprioceptors, it modulates commands to motor neurons to compensate for shifts in body position or changes in load upon muscles. The cerebellum is important for making postural adjustments in order to maintain balance. The cerebellum is involved in the following functions: Motor commands are not initiated in the cerebellum rather, the cerebellum modifies the motor commands of the descending pathways to make movements more adaptive and accurate. Historically, the cerebellum has been considered a motor structure, because cerebellar damage leads to impairments in motor control and posture and because the majority of the cerebellum’s outputs are to parts of the motor system.

Although the cerebellum accounts for approximately 10% of the brain’s volume, it contains over 50% of the total number of neurons in the brain. All rights reserved.The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a structure that is located at the back of the brain, underlying the occipital and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex (Figure 5.1). Further, to investigate the efficacy of essential oil preparations compared to usual analgesics (paracetamol or acetylsalicylicacid) a double blind, placebo controlled, randomized study should be performed.Ĭopyright © 1995 Gustav Fischer Verlag, Struttgart
The essential plant oil preparations can thus be shown by laboratory tests to exert significant effects on mechanisms associated with the pathophysiology of clinical headache syndromes. A significant analgesic effect with a reduction in sensitivity to headache is however produced by the combination of peppermint oil and ethanol. The combination of peppermint oil, eucalyptus oil and ethanol can increase cognitive performance while having a muscle-relaxing and mentally relaxing effect, but has little influence on pain sensitivity. The treatment effect of the preparations was evaluated by comparing baseline and treatment measurements. The test preparations were applied to large areas of the forehead and temples using a small sponge.
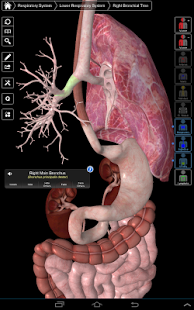
#ESSENTIAL ANATOMY 3 TRIAL PLUS#
Four different test preparations were used: preparation 1 (LI1701) consisted of 10 g peppermint oil and 5 g eucalyptus oil plus ethanol 90% to 100 g preparation 2 (LI1702) of 10 g peppermint oil and traces of eucalyptus oil plus ethanol 90% to 100g preparation 3 (LI1703) of traces of peppermint oil and 5 g eucalyptus oil plus ethanol 90% to 100 g and preparation 4 (placebo) of traces of peppermint oil and traces of eucalyptus oil plus ethanol 90% to 100 g.
Therefore the effects of peppermint oil and eucalyptus oil preparations on neurophysiological, psychological and experimental algesimetric parameters were investigated in 32 healthy subjects in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized cross-over design. Assuming that a clinical relevant analgesic action exists, this ought to be observable in experimental algesimetric human tests.
#ESSENTIAL ANATOMY 3 TRIAL SKIN#
It is also known that peppermint oil induces a significant increase of the skin blood flow of the forehead after local application, measured by laser doppler. Further it was shown that peppermint oil inhibits non-competively 5-hydroxytryptamin (Serotonine) and substance P induced smooth muscle contraction in animal-models. Local application of peppermint oil generates a long-lasting cooling effect on the skin, caused by a steric alteration of the calcium channels of the cold-receptors. Especially for peppermint oil certain analgesic mechanisms were recently described. The rationale for using essential oils to alleviate headache is based on several assumptions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
